UNDERSTANDING THE KEY SYSTEMS
FLEXIBILITY
Monetizing B2B (Business-to-Business) software involves various strategies to generate revenue. The choice of strategy obviously depends on the nature of the software and the target market, among others. As business requirements are constantly evolving, flexibility is critical for successful monetization.
YOUR APPLICATION – LICENSING & ANALYTICS – INVOICING
This flexibility is usually attained, by decoupling the application core from the licensing and analytics system, e.g., SLASCONE, and the billing/invoicing system(s).
While SLASCONE is not a billing/invoicing system, it dramatically enhances your monetization options, by leveraging its usage analytics functionality.

FLEXIBLE MONETIZATION – SYSTEM WORKFLOW
The objective of this section is not to delve into the specifics of monetization models (this is covered here). Instead, to highlight how the workflow between the core, licensing, and invoicing system may differ. For the sake of simplicity, let’s differentiate between flat and consumption-based systems.
Flat
Flat systems are typically characterized by the lack of consumption-based components. In other words, the monthly or yearly fee does not change without an explicit upgrade or downgrade.
In such cases, the workflow is pretty trivial. The change (e.g., upgrade, downgrade, cancellation) takes place in a back-office system, and is then propagated to the licensing system in order to reflect this change in the application. No usage data is involved.
Consumption based
Consumption-based (or transaction-based) models are characterized by at least one variable component. The yearly or monthly fee of this component depends on its actual usage.
In such cases, SLASCONE collects the usage data and forwards it to the invoicing system according to the billing cycle. It is important to highlight that there is no direct communication between the software core and the invoicing system.
SEAMLESS TRANSITION TO CONSUMPTION BASED
Amidst all the hoopla surrounding consumption-based monetization in recent years, it’s important to note that not all application types are ideal for it. Especially in enterprise B2B agreements, a flat fee is very often preferred for both sides.
On the other hand, introducing a consumption-based model might be daunting, especially for established vendors, wary of its repercussions. This is where SLASCONE’s usage analytics module comes into play, facilitating a seamless, risk-free transition.
Let us use an example to clarify this: A software vendor of a document processing application is considering a model based on the number of processed documents. Until now, a flat model has been in place. There are many possible variations of such consumption based models, as explained here.
Regardless of this, the vendor can (or rather should) start collecting and analyzing consumption usage data with SLASCONE before making any business model decisions. Following a few days, weeks, or months of collecting actual usage data, better, fact-based decisions can be made.
FEATURES
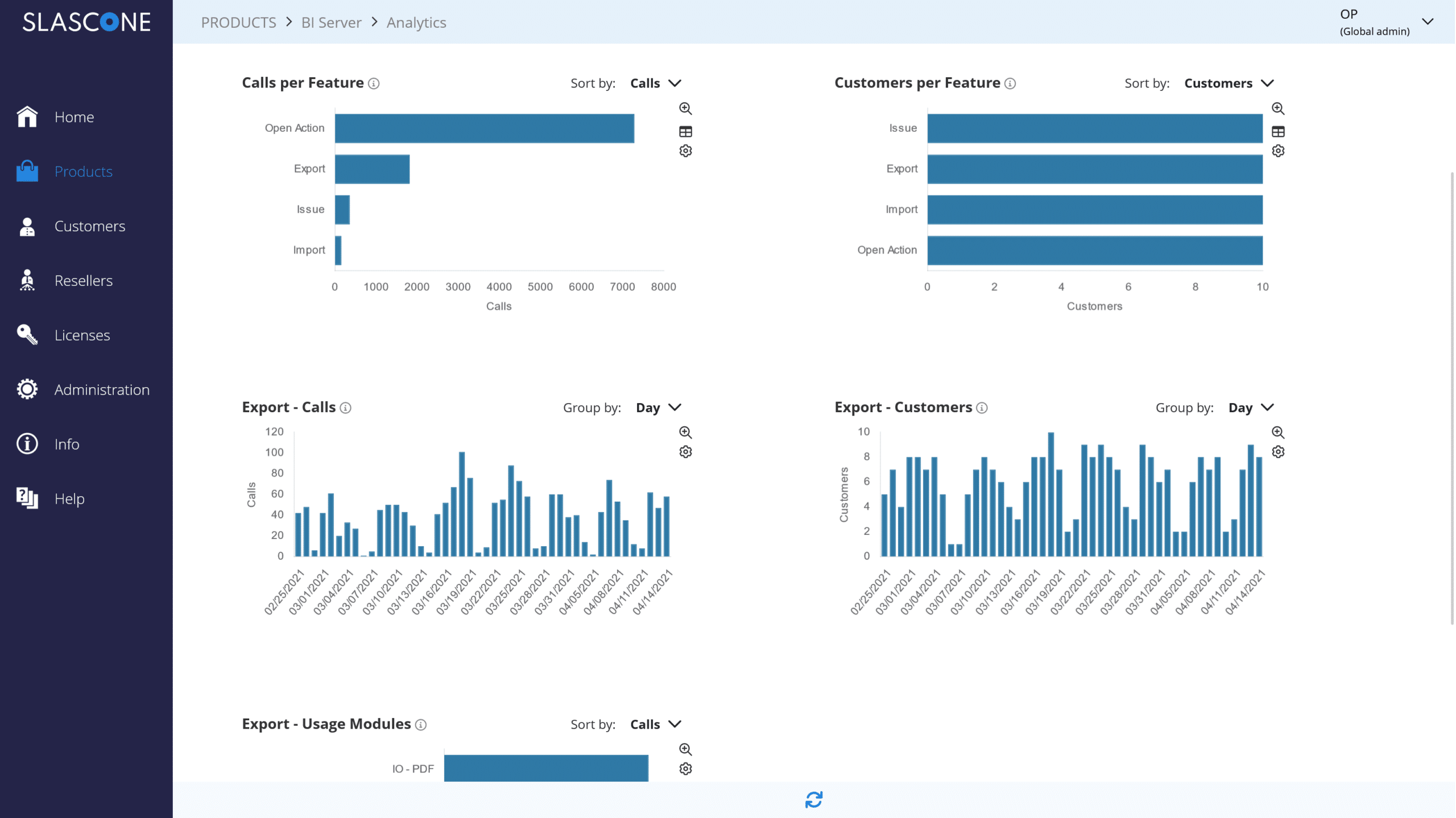
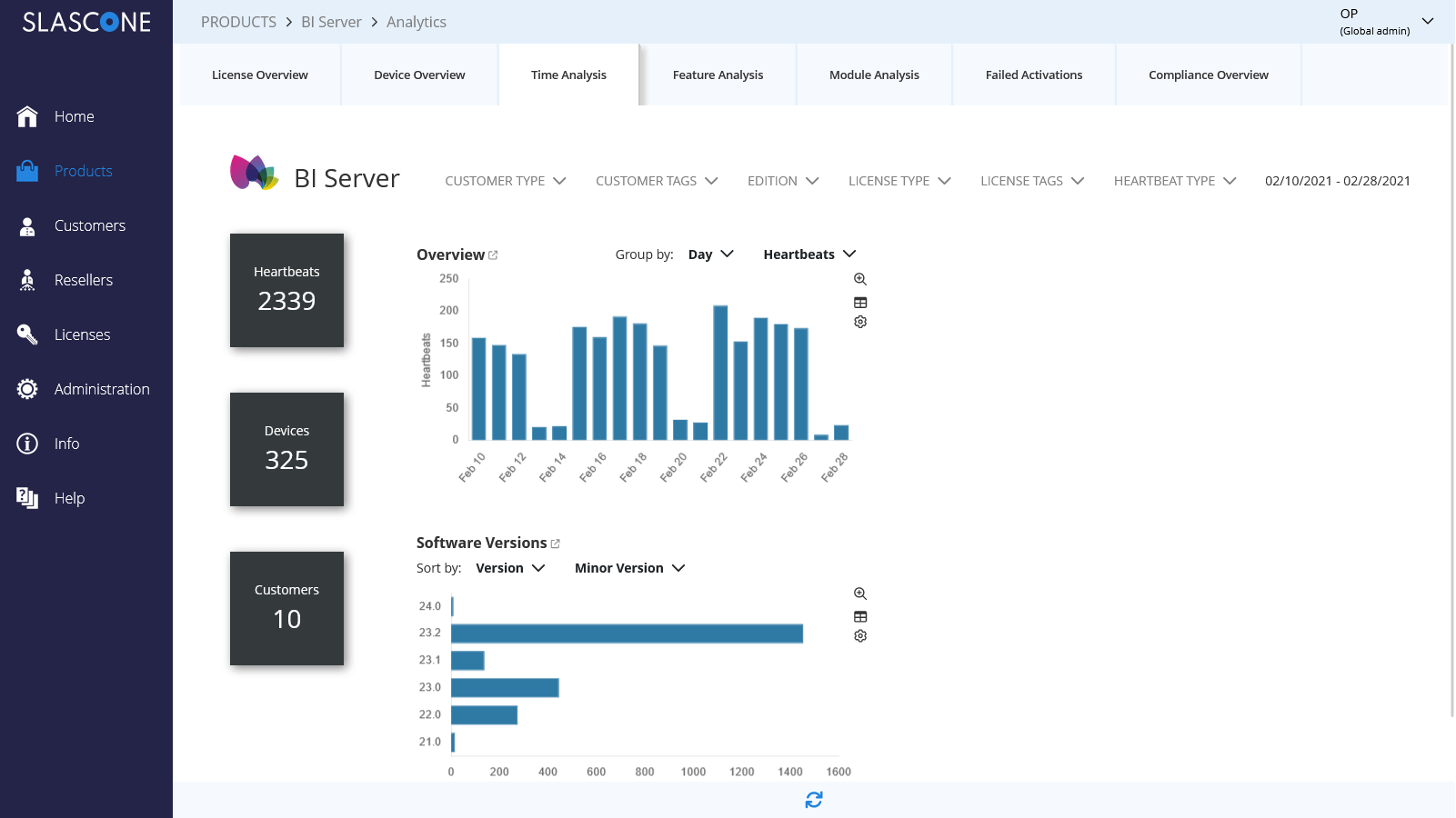
Collect Usage data
Analyze the actual usage of your product’s features or modules. Identify trends and patterns.
Soft and Hard Limits, Alerts
Decide how to handle over usage. Inform users in real time as soon as X% of the quota has been reached.
Quota Pools
Assign quotas to a single user/device or to a pool of users/devices.
Monetization Analytics
Collect and send usage data to your invoicing monetization system.